Knowledge‐Based Wastewater Decision Support System (WWDSS)
2012 - 2016 • Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH
Purpose
Water and Wastewater Management Programme- GIZ in Egypt
Activities
WWDSS allows for improving project selection and optimising portfolios through increased coherence between national policies, sectorial policies, resource allocation and spending practices, and improved knowledge management. Utilizing WWDSS to identify cost‐efficient interventions in the wastewater sector and utilize it as a platform for strategic advice and monitoring of the financial performance of the ACs is done as follows:
1. According to the community needs (centralized /Decentralized services, unserved communities) the service areas are defined using the cluster optimization module is used to define a List of target villages, cost estimate for cluster, financial/economic viability and sustainability.
2. The unit cost module is then used to calculate the Quantity survey and unit cost for different elements and material of WW projects
3. The Financial module -at project level- is used to calculate the financial costs (CAPEX/OMEX) and revenues of the of the new projects
4. The financial module –at the national level- simulates the financial consequences and assess the financial viability of WW investment planning alternatives and their impact on the financial statement of the ACs
5. The wastewater reuse module is used to define the different possible treated wastewater reuse options, best options, the revenue of each option, estimation of the required investment, O&M costs
6. The sludge reuse module is used to define the different possible treated wastewater reuse options, best options, the revenue of each option, estimation of the required investment, O&M costs
7. The fund raising module helps in match making between funding agencies (local and international) and the projects seeking funds.
8. The management module helps in proposing the best approach to wastewater management projects
9. The economical predicts the socio-economic benefits at ACs, development and employment opportunities, & potential economic growth that goes with it
10. The Priorities & Investment Planning Module is used to prioritized the projects implementation accordion to the allocated investments, environmental, demographic, social, operational criteria at local and national levels.
11. Upon approving the fund, tendering documents are prepared by the MPU staff. And upon the Monitoring & Evaluation Module is used during the implementation of the project.
12. The database module stores detailed data about demographic structure, Existing wastewater infrastructure, under construction projects and planned in each ACs in a chronological historical order. The databases of the 23 ACs are linked via a wide area network (VPN).
13. A video conferencing that communicate the 23 ACs with the HCWW is now available through the VPN alongside the internet access.
WWDSS is adapted to a more complex environment, broadening the comprehensiveness of decision making, and aligning it to programme‐based approach (PBA), which help streamline the efficiency of its operations and improve organisational knowledge, thus increasing value for money. These achievements translate into sustained impact on health, sanitation, irrigation and by extension enhance agricultural outputs and food security.
Images
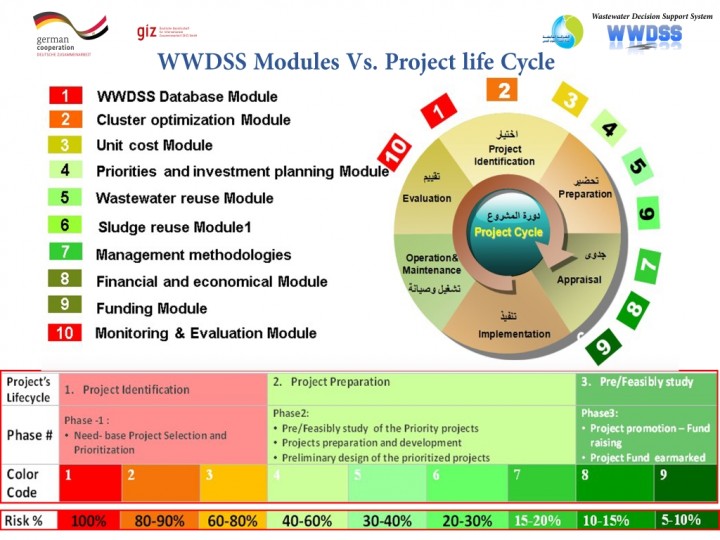
Image: The Toolbox of WWDSS, which composed of 11 computer-based modules that can be implemented either stand alone or integrated, projected on the 6 phases of the project management life cycle , alongside the measure of the percentage of "risk reduction" a
Countries of activity
Location of main activity
Objectives
1. To serve as a Guiding Decision Support System (DSS) for any kind of future investments in the wastewater sector;
2. To provide different scenarios or alternatives for scheduling as well as reducing the required investments and the impact of future investments on future Operations and Maintenance (O&M) costs and hence the financial performance of the ACs and the HCWW;
3. To provide different scenarios for reducing the O&M costs and increasing the revenues, to prepare a list of investment projects that need funding, Initial feasibility studies with reasonable details for prioritized projects, Fund raising from local &international investors;
4. To stores technical, financial, and demographic data necessary and provides accurate, reliable, secured, and safe information retrieval;
5. To provides cost estimations of wastewater services, provision components in Egypt,;
6. To helps in the evaluation of alternative priority investment options, and contribute to the preparation of 5‐year wastewater investment plans, up to year 2037;
7. Helps in the development of a participatory, planning approach with the rest of the ministries and relevant bodies at the national level to achieve, the national plan Improves the image and credibility of the Affiliated companies with consumers;
8. Strengthening current capacities of the technical staff in the 23 affiliated wastewater companies (ACs);
9. Support and enabling the holding company for water and wastewater HCWW and ACs role in prioritizing, implementing and managing investments in the wastewater sector;
10. To identify cost‐efficient interventions in the wastewater sector and utilize it as a platform for strategic advice and monitoring of the financial performance of the ACs; and
11. provide practical solutions, considering the significant and urgent need of expanded and improved wastewater services, which is constrained by the overall fiscal situation in Egypt.
Further information
1. The HCWW, in cooperation with GIZ implemented the bottom‐up approach in developing the WWDSS by engaging respective professional , and junior/middle management staff of all the 23 ACs in each step, in order to ensure the sustainability of the system; create ownership of the ACs and HCWW towards the WWDSS; build the capacities of the personnel in the ACs, and effectively assist during project execution and beyond the assignment period.
2. Each ACs of the 23 companies, is equipped with a server and 4 PCs, by which a LAN is built to supports the multiuser operation of the system and guarantee its sustainability.
3. A VPN –based Wide Area Network (WAN) is built, links 23 governorate allover Egypt , and covers the needs for greater exchange of information, sharing of knowledge, coordinate a wide range of decisions on a local and national level, and increase in stakeholder dialogue and stakeholder-sensitive decision-making.
Contact information
Dr. Gamal Abdel Moaty
Login to see the e-mail-adress of the contact person.
Filter tags
Capacity development Cities Enabling environment and institutional strengthening German government Market development Middle East & North Africa Peri-urban Public awareness, advocacy and civil society engagement Treatment of wastewater or greywater Urban (entire city)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH
Eschborn
Germany
Uploaded by:
SuSanA Admin (susanaadmin)
















